The Universal Serial Bus (USB) is vital to modern technology. It serves as a standard interface for personal computers and consumer electronics, enabling smooth digital data communication. USB ports are designed for short-distance digital data communication, enabling devices to connect and transfer data using USB cables.

Since its development in the 1990s, USB has evolved alongside computer technology, becoming smaller, faster, and more powerful. Its user-friendly, plug-and-play functionality allows for the easy addition and removal of devices, eliminating the need for manual configuration when connecting peripherals like printers, scanners, and digital cameras.
The different types of USB connectors – A, B, and C – each play a unique role in the vast landscape of electronic devices we use daily.
Key Takeaways
- USB interface is a standard connection for various electronics, facilitating smooth digital data communication.
- The evolution of USB has resulted in faster and more robust connections, greatly enhancing electronic device capabilities.
- The plug-and-play nature of USB interfaces simplifies device connections and improves user experience.
Understanding USBs
In the world of computer peripherals and devices, you will come across USB interfaces quite often. The origin of USB dates back to 1996; it was introduced as a standard interface to connect peripherals like printers and scanners to personal computers.
Over time, USB has evolved and now comes in various versions and types, including USB 1.1, USB 2.0, USB 3.0, USB 3.1, USB 3.2, and the latest standard, USB4.

USB 1.1 is the older version of USB, supporting data transfer rates of up to 12 Mbps. This standard was commonly used in older technology. USB 2.0, on the other hand, was a significant improvement, allowing transfer speeds of up to 480 Mbps. You'll often find USB 2.0 ports on various devices.
As technology advanced, so did USB standards, although their naming conventions can be a bit confusing. Initially, USB 3.0 was introduced with up to 5 Gbps transfer speeds. USB 3.0 was later rebranded as USB 3.1 Gen 1, while what was originally termed USB 3.1, capable of up to 10 Gbps data transfer, became known as USB 3.1 Gen 2.
USB 3.2 further built on this, supporting up to 20 Gbps. These standards, also known as USB 3.x, brought improved power efficiency and better backward compatibility, following the naming conventions set by the USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF).
The latest evolution in USB technology is USB4, supporting up to 40 Gbps data transfer speeds. It offers increased power delivery and the ability to simultaneously operate multiple data and display protocols.
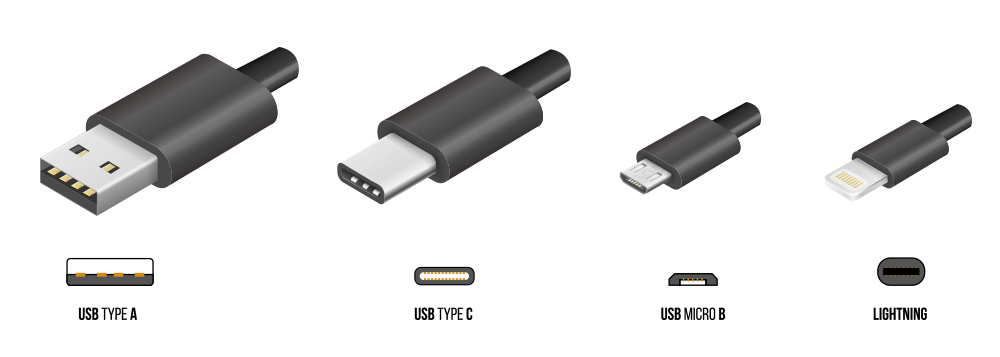
Another critical aspect to consider regarding USB interfaces is the variety of connector types. The most common are Type-A (standard rectangular shape), Type-B (square shape, typically used in printers), Type-C (reversible, slim, and oval-shaped), and even the older Mini and Micro connectors. Among these, USB-C is the most versatile, supporting high-speed data transfer, power delivery, and display port functionality.
Versions labeled with the "SS" abbreviation, such as USB 3.0 SS, stand for SuperSpeed and indicate higher transfer rates compared to USB 2.0. Similarly, the first and second generations of USB 3.2 support up to 5 Gbps and 10 Gbps, respectively.
Types of USB Connectors
When dealing with USB interfaces, you will come across various connectors. This section briefly overviews the main USB connector types: USB-A, USB-B, Micro-USB, and USB-C.

USB-A: USB-A connectors are the standard flat and rectangular USB interface you encounter in various devices. Your computers, game consoles, TVs, and peripherals often feature USB-A ports. These cables typically have a USB-A connector on one end, connecting to the host devices, and another type of connector (such as USB-B or Micro-USB) on the other end to connect to peripherals.
USB-B: Type B connectors have a squarish shape and are used primarily for connecting peripherals, such as printers, scanners, and external hard drives, to a computer. USB-B cables typically have a USB-A connector on one end and a USB-B connector on the other, making it easy to distinguish and use appropriately.
Micro-USB: As the name suggests, Micro-USB connectors are a smaller version of the standard USB connectors. They are commonly found in mobile devices such as smartphones, tablets, and portable chargers. Micro-USB cables generally have a USB-A connector on one end and a Micro-USB connector on the other.
USB-C: Introduced in 2014, USB-C is a more recent and versatile connector type designed to replace USB-A and USB-B connectors. The critical advantage of USB-C is its reversible design, which allows you to plug it in either way.
USB-C cables can facilitate a wide range of functionalities, including fast charging, high-speed data transfer, and support for video output. You'll find USB-C connectors in various modern devices, such as laptops, smartphones, and even Apple products that previously used a Lightning connector.
USB Speed - Data Transfer and Power Delivery
USB, or Universal Serial Bus, is a widely used interface that enables easy charging and data transfer between devices. In this section, you'll learn about USB speeds and how power delivery works.

USB has evolved, with technological advancements resulting in smaller, faster, and more powerful iterations. USB speeds range from 12 Mbps in USB 1.0 to 40 Gbps in the latest USB4 standard. USB 3.0, also known as SuperSpeed USB, introduced a new architecture and protocol that allows for full-duplex data transfers at 5 Gbps, referred to as Gen 1. Subsequent releases, such as USB 3.1 and USB 3.2, increased data transfer rates to 10 Gbps and 20 Gbps, respectively.
Power delivery is an increasingly important aspect of modern USB technology. While standard USB-C ports can offer up to 15W of power—assuming the charger can deliver 3A of current—USB Power Delivery (USB PD) significantly extends these capabilities.
USB PD enables a more flexible power management system and can provide up to 100W of power to compatible devices. This higher power capacity opens the door for charging larger electronics like laptops, making USB-C with USB PD an incredibly versatile connector for both data transfer and power delivery.
Regarding connectors, USB Type-C is prevalent in modern devices due to its versatility and support for faster data transfer and power delivery. A USB Type-C connector contains four pairs of pins, or 'lanes,' dedicated to transmitting and receiving data. USB 3.0 and 3.1 utilize one transmitting lane and one receiving lane, while USB 3.2 takes advantage of all four lanes to achieve its 20 Gbps data rate.
In summary, USB interfaces offer various speeds and power delivery options, catering to various devices and use cases. With advancements such as USB4 and USB PD, you can expect even more powerful and efficient data transfers and charging capabilities, resulting in better performance and convenience for your devices.
Why is USB so Popular?
USB, or Universal Serial Bus, has become the most dominant interface in the world of technology, and its popularity can be attributed to several key factors. One of the reasons for its widespread acceptance is its ease of use.
The evolution of USB over the years has also contributed to its success. With the advent of Gen 1 and Gen 2, the performance and capabilities of USB have significantly improved. These upgrades have allowed USB to offer faster data transfer rates, more efficient power delivery, and better overall performance.
Another reason USB is so popular can be attributed to collaboration and standardization. Major technology companies such as Intel, IBM, Compaq, DEC, and Nortel came together to support and develop USB under the leadership of Ajay Bhatt. This partnership ensured that USB would be universally accepted and implemented as a standard interface across different platforms and devices.
USB's versatility is a critical factor in its popularity as well. You can use USB to connect various types of devices, from external storage drives and keyboards to smartphones and cameras. Its adaptability has made it an essential part of modern technology, with the availability of numerous connector types catering to an extensive range of gadgets.
USB Role in Modern Tech
USB, or Universal Serial Bus, is indispensable to today's technology ecosystem. It serves as a versatile connection interface between a wide array of devices. With its plug-and-play nature and hot-swapping capabilities, USB makes it incredibly easy for you to connect and start using your devices instantaneously.

In gaming, game consoles have adopted the USB interface for various purposes. USB has become a standard across the industry, from connecting controllers and charging their batteries to powering external hard drives and other peripherals. The convenience of a unified connectivity option ensures it remains the go-to choice for gamers and developers alike.
Similarly, monitors have also started incorporating USB technology. Modern monitors not only support HDMI and DisplayPort but also USB-C connections. This flexible option eliminates cable clutter on your desk, as a single USB-C cable can simultaneously transmit video signals, power, and data.
USB technology also excels in providing Ethernet connectivity options. Adapters can convert USB ports into Ethernet ports, enabling you to connect your devices directly to a wired network easily. These adapters are beneficial, especially for ultrabooks and tablets that often forego Ethernet ports to save space. This means you can enjoy stable and high-speed wired internet connections on your devices without hassle.
Additionally, USB technology supports hot-swapping, allowing you to safely connect and disconnect devices while your computer is running. This feature is invaluable for those who need to switch between different peripherals quickly, such as photography professionals who need to transfer files from various storage formats.
In conclusion, USB has played a crucial role in shaping modern technology by providing a versatile and user-friendly interface for various devices. Its plug-and-play nature, hot-swapping capabilities, and adaptability to various needs have made it a cornerstone in today's tech world. As technology continues to evolve, it's clear that the USB interface will remain an essential part of our digital lives.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How do USB interfaces transfer data between devices?
USB interfaces facilitate short-distance digital data communication by allowing devices to connect and transfer data via standard Universal Serial Bus (USB) cables.
2. What are the different types of USB connectors?
There are several types of USB connectors, including:
- USB Type-A is thestandard and most commonly used connector on computers, laptops, and various peripherals.
- USB Type-B:A square-shaped connector mainly used on printers and scanners.
- USB Mini and Micro:Smaller connectors are used primarily on mobile devices and portable electronics.
- USB Type-C:A newer, reversible connector that supports faster data transfer rates and increased power delivery, typically found on new laptops, smartphones, and other devices.
3. What are the main advantages of using a USB interface?
The main advantages of using a USB interface are ease of use, universality, and compatibility. USB connectors offer plug-and-play functionality, requiring minimal setup, and can be used with various devices. Additionally, the USB standard has primarily replaced other connectors, making it the preferred choice for connecting different devices.
4. How do USB versions affect transfer speed and compatibility?
USB versions vary in terms of transfer speed and compatibility. Some of the standard USB versions are:
- USB 1.1: This version can reach a maximum transmission rate of 12 Mbps (Full Speed).
- USB 2.0: Provides faster data transfer rates up to 480 Mbps and is compatible with most USB devices and cables today.
- USB 3.0 and later: Offers significantly improved transfer speeds (up to 20 Gbps in USB 3.2) and enhanced power delivery while maintaining backward compatibility with older USB versions.
5. In what ways can USB interfaces be used in laptops?
USB interfaces can be used in laptops for various purposes, including:
- Connecting peripheral devices, such as keyboards, mice, and cameras.
- Transferring data to and from external storage devices, like flash and hard drives.
- Charging smartphones and other devices with a USB connection.
- Connecting to displays and monitors using USB-C or a USB-to-video adapter.
6. What are the primary roles of a USB cable in connectivity?
USB cables serve several primary functions:
- Providing a physical connection between USB devices.
- Facilitating data transfer between connected devices.
- Delivering power to charge devices or supply energy to peripherals.
- Offering compatibility with different USB versions and connector types, depending on the specific cable.
Order USB Cables from Us in Bulk

To order USB cables in bulk, please contact us using the customer contact form. We offer fast delivery to all global locations.